By Sophia Mavrou,
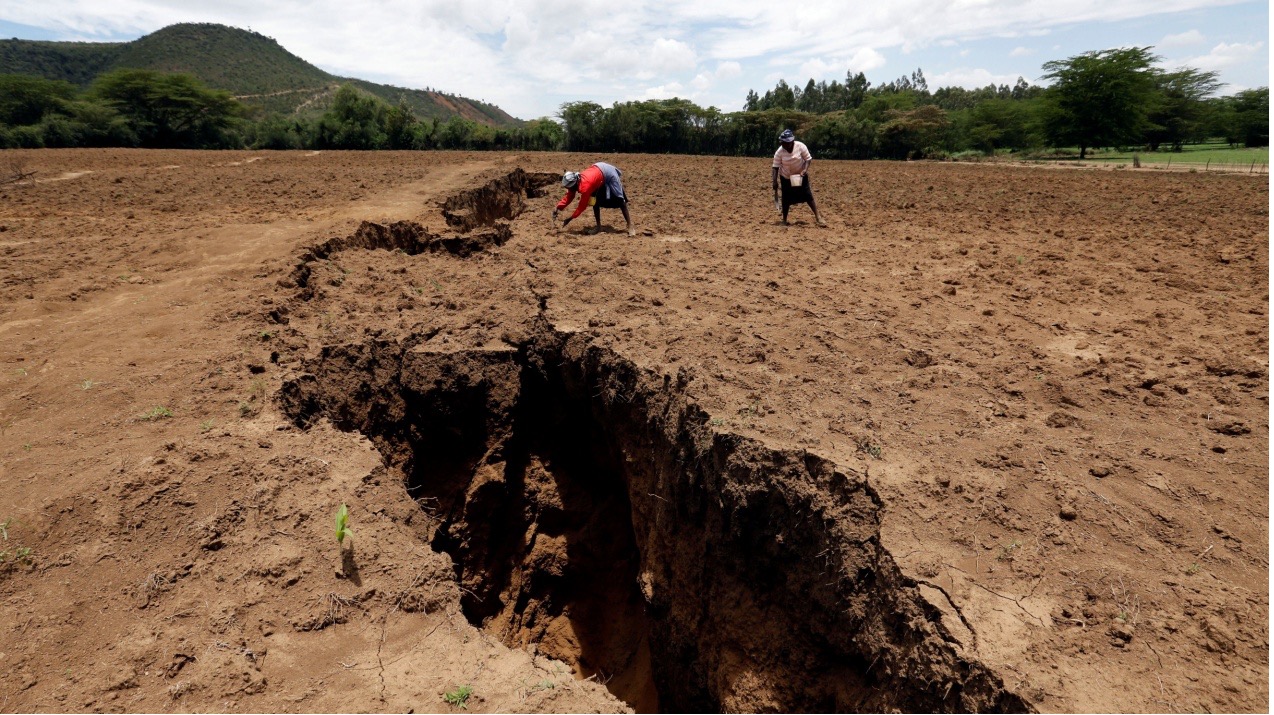
Photographs show that Africa is currently being split up by a 35 kilometer rift, which will give its place to a new ocean in the region of Kenya. Although changes like this take five to ten million years to be completed, scientists are confident enough that African countries like Zambia and Uganda could potentially have their own coastlines. This scenario could render a fiction film the next Hollywood blockbuster, but it is more likely to turn into a quite realistic documentary.
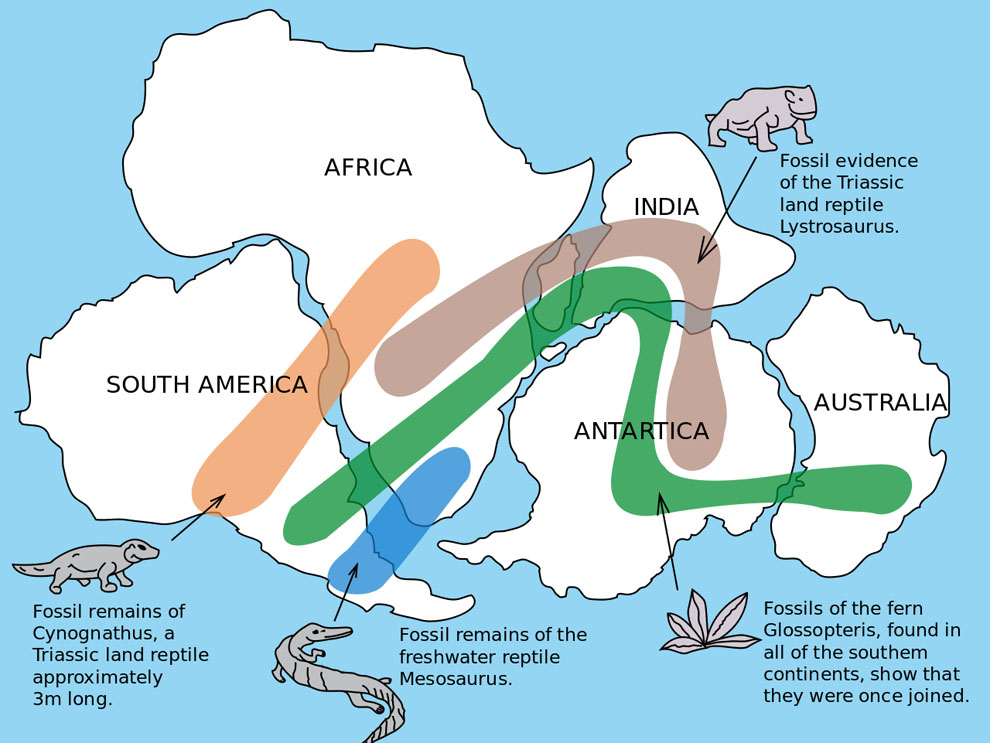
The earth’s tectonic plates have not ceased moving for over 4 billion years. The continent of Africa has attracted the scientific attention for a long time, given that it has gone through major transformations over the years. Let’s not forget that it was glued to South America alongside with Northern Europe, nearly 150 million years ago. The contemporary crack initiated in the sea’s bottom near to the Afar region in Northern Ethiopia at approximately thirty million years ago and moved southwards towards Zimbabwe at a mean rate of between 2.5-5cm a year.
There is still no a straightforward answer to the question “What kind of mechanism is responsible for that drift?” Presumably, the extensional forces generated at the boundaries of the tectonic plates at the bottom of the ocean are one part of the answer. Yet, it is not the only one. What is more and with regard to the formation of a new sea, Ken Macdonald, a marine geophysicist and a professor emeritus at the University of California, supports that “The Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea will flood in over the Afar region and into the East African Rift Valley and become a new ocean, and that part of East Africa will become its own separate small continent”.
A phenomenal alteration such as this requires the evacuation of people who inhabit regions close to the rift. Unquestionably, residents of the areas of Kenya, Ethiopia, Tanzania and East Africa at large, anticipate large catastrophic earthquakes, abrupt motorway-splitting faults and are ready to make adjustments to their cultivations. Nonetheless, the emergence of a sixth ocean will apparently influence the financial growth of the area. That is, amplify the production of the fertile land, rejuvenate the breeding ground, attract tourists from all over the world and generally speaking impact the future of the whole world.
The consequences of such phenomenal continental break-ups, could be abrupt motorway-splitting faults or large catastrophic earthquakes, but usually it goes about splitting continents without anybody even noticing. As mentioned before, Africa will be split no sooner than 5 million years. Hence, we do not stand a chance of witnessing the final result, but we get a glimpse of it by examining its once-in-a-life-time process.
References
-
The Big Break-up: How Africa is gradually splitting into two continents and giving rise to a new ocean. firstpost.com. Available here




